Where Are We Headed with sugar cane products in Consumer Demand
Where Are We Headed with sugar cane products in Consumer Demand
Blog Article
A Deep Dive Into Sugar Cane: Insights on Production, Material, and Product Advancement
Sugar cane plays a vital function in farming, underpinning economies in tropical areas. Its farming involves detailed processes influenced by different ecological factors. Nonetheless, growers deal with considerable obstacles, including climate adjustment and market variations. Technologies in item advancement are arising in reaction to advancing customer needs. Understanding these characteristics is vital for comprehending the future of this important crop and its influence on worldwide markets. What lies in advance for sugar cane and its myriad applications?
The Value of Sugar Cane in Global Agriculture
Sugar cane functions as a crucial plant in global agriculture, underpinning economies and food systems in numerous tropical regions. This functional plant is primarily cultivated for its high sucrose content, which is improved right into sugar, a standard ingredient in many foodstuff. Past sweetening, sugar cane is additionally crucial for creating biofuels, especially ethanol, adding to energy sustainability.The financial value of sugar cane reaches employment, giving incomes for numerous farmers and workers in processing centers. In several nations, sugar cane farming and processing stand for significant parts of agricultural GDP, influencing profession equilibriums and regional development.Additionally, sugar cane's adaptability to numerous environments enhances its importance as a plant, making sure constant supply in worldwide markets. Its by-products, consisting of molasses and bagasse, even more diversify its utility, making it a crucial element in food, energy, and sector. In general, sugar cane remains a foundation of agricultural performance worldwide.
Growing Procedures: From Planting to Harvest
Growing sugar cane entails a series of well-defined processes that assure suitable growth and return. The cultivation starts with land prep work, where the dirt is tilled to secure ideal oygenation and drainage. Following this, seed cane, which contains mature stalks, is selected and cut into sectors (sugar cane products). These segments are then grown in furrows, making sure correct spacing to enable for sunlight and nutrient access.Once grown, irrigation systems are used to maintain ample moisture degrees, as sugar cane flourishes in damp problems. Weeding and pest monitoring are necessary throughout the expanding period to lessen competitors for resources. Nutrient application, consisting of plant foods, sustains robust growth. As the plants mature, keeping an eye on for illness and insects continues.Harvesting usually happens 10 to 24 months post-planting, relying on the selection. The canes are cut short, ensuring very little waste, and are swiftly transported for processing to protect sugar high quality
Geographic Circulation of Sugar Cane Production
The geographic distribution of sugar cane production is mainly formed by details environment and dirt requirements. Major creating countries, such as Brazil, India, and China, take advantage of tropical and subtropical climates that support the crop's growth. Comprehending these elements supplies insight right into the international landscape of sugar cane farming.
Major Producing Countries
Sugar cane is grown in different areas worldwide, certain nations control production due to positive environments and agricultural methods - sugar cane products. Brazil leads the worldwide market, representing around one-third of overall production, thanks to its comprehensive vineyards and progressed farming strategies. India complies with as a substantial producer, taking advantage of both positive climate condition and a big domestic market. China and Thailand likewise rank among the leading manufacturers, with well-established facilities sustaining their sugar industries. Other remarkable factors include the United States, Mexico, and Australia, each leveraging their one-of-a-kind farming systems to improve output. These nations play an important role in the sugar cane supply chain, affecting global rates and availability
Climate and Dirt Requirements
Perfect climate and dirt conditions are important for successful sugar cane production. Sugar cane thrives in exotic and subtropical regions, needing cozy temperature levels between 20 ° C and 30 ° C (68 ° F to 86 ° F) These plants need abundant sunlight and rainfall, ideally in between 1,500 to 2,500 millimeters each year, to guarantee peak development. The dirt must be well-drained, abundant, and abundant in natural matter, with a pH degree preferably between 5.5 and 8.5. Sandy loam or clay loam soils are specifically for sugar cane cultivation, offering essential nutrients and drain. Geographical distribution is greatly affected by these variables, with significant production locations situated in Brazil, India, and China, where environmental conditions line up with the plant's needs for development and return.

Obstacles Faced by Sugar Cane Growers
Sugar read the article cane cultivators run into considerable challenges go right here that affect their resources. Environment modification presents unpredictable weather patterns, impacting plant return and quality. Furthermore, market rate volatility develops financial unpredictability, complicating lasting preparation for these agricultural manufacturers.
Climate Modification Impacts

Just how do environment adjustment effects impact the feasibility of sugar cane growing? Rising temperatures and unpredictable weather condition patterns significantly challenge sugar cane farmers. Boosted warm can lead to reduced returns, as the plants struggle to thrive in severe conditions. Furthermore, modified rainfall patterns result in either dry spells or excessive flooding, both harmful to plant health and wellness. Insects and diseases are likely to multiply in warmer environments, even more harmful production. Furthermore, soil degradation and salinization as a result of rising sea degrees can reduce arable land. These climatic modifications urge cultivators to adjust their techniques, typically requiring financial investment in new innovations and resilient crop selections. Ultimately, the sustainability of sugar cane farming pivots on addressing these climate tests successfully.
Market Cost Volatility
Market cost volatility offers significant challenges for sugar cane cultivators, influencing their monetary security and planning. Fluctuations in market rates, driven by elements such as worldwide supply and need, weather conditions, and government plans, produce uncertainty for producers. This unpredictability makes it challenging for growers to forecast earnings and take care of general expenses successfully. In addition, when prices go down all of a sudden, many farmers may battle to cover production costs, resulting in prospective economic distress. To alleviate these threats, some farmers transform to contracts or hedging approaches, yet these options may not come to all. Market cost volatility stays a persistent worry, influencing the overall sustainability and productivity of sugar cane farming.
Recognizing the Sugar Cane Supply Chain

Market Fads Affecting Sugar Cane Rates
The dynamics of sugar cane rates are affected by a selection of market patterns that reflect wider financial problems and customer actions. International demand for sugar and sugar-related products plays a necessary function, with boosting rate of interest in natural and sustainably sourced products driving costs higher. Additionally, changes in oil costs influence the price of production and transport, additional influencing market rates. Weather patterns are another significant variable; damaging problems can bring about minimized yields and enhanced prices. Profession plans, tolls, and global arrangements additionally form the marketplace landscape, impacting supply chains and availability. Money exchange rates can complicate worldwide profession, impacting prices for both exporters and importers. Lastly, shifts in consumer choices towards much healthier alternatives might alter demand patterns, developing a ripple impact on sugar cane prices. Comprehending these interconnected trends is crucial for stakeholders in the sugar industry.
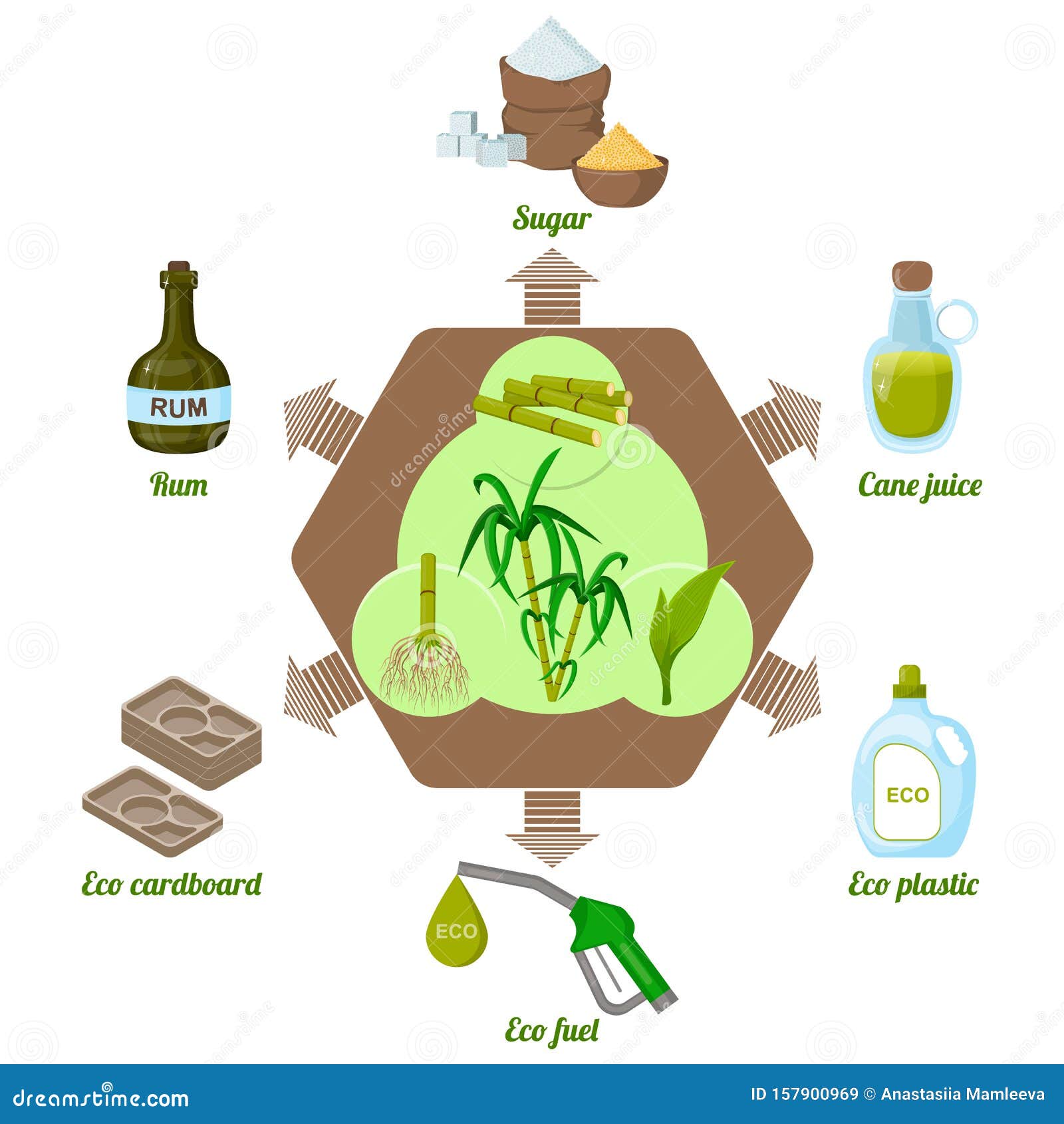
Innovations in Sugar Cane Item Development
Many innovations in sugar cane product growth are reshaping the industry and broadening its applications. weblink Researchers are checking out alternative uses beyond traditional sugar, including biofuels, naturally degradable plastics, and health supplements. Advancements in enzymatic handling techniques have enhanced the removal of useful compounds such as antioxidants and vitamins from sugar cane, promoting its usage in useful foods.Additionally, the growth of genetically customized sugar cane ranges aims to enhance return and resistance to parasites, while likewise boosting the nutritional profile of the crop. Technologies in fermentation processes have led to the production of high-quality liquors originated from sugar cane, interesting an expanding market for craft spirits.Moreover, sustainable techniques in cultivation and handling are gaining grip, with a concentrate on reducing ecological impacts. These improvements not just develop new market chances but likewise foster a more sustainable technique to sugar cane production, aligning with worldwide patterns in the direction of environment-friendly products.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Environmental Influences of Sugar Cane Farming?
The environmental impacts of sugar cane farming consist of deforestation, loss of biodiversity, water pollution from plant foods and pesticides, soil degradation, and greenhouse gas exhausts, all of which significantly add to eco-friendly discrepancies and environment change.
How Does Sugar Cane Farming Affect Resident Economies?
Sugar cane farming considerably influences neighborhood economies by developing work, promoting farming fields, and producing earnings for farmers. It can additionally lead to economic reliance and variations based on market demands and ecological conditions.
What Are the Main Pests and Diseases Affecting Sugar Cane?
The main insects affecting sugar cane include the sugarcane borer and aphids. Illness such as red rot and smut significantly influence yield. Farmers have to execute incorporated pest administration approaches to reduce these dangers successfully.
How Is Sugar Cane Processed Into Different Products?
Sugar cane processing includes crushing the stalks to remove juice, followed by explanation, evaporation, and condensation. This procedure returns raw sugar, molasses, and ethanol, each serving unique objectives in various industries, from food to power.
What Are the Nutritional Aspects of Sugar Cane?
The dietary facets of sugar cane include vital nutrients, specifically B vitamins, calcium, and iron. It also includes fiber, though mostly made up of sucrose, which gives energy however does not have significant nutrients.
Report this page